Customer Success - Gran Telescopio Canarias
The World's Largest Optical Telescope Relies on VxWorks
The Gran Telescopio Canarias enables scientists to view the furthest and palest cosmic bodies in the universe.
Customer Success Story
The Objective
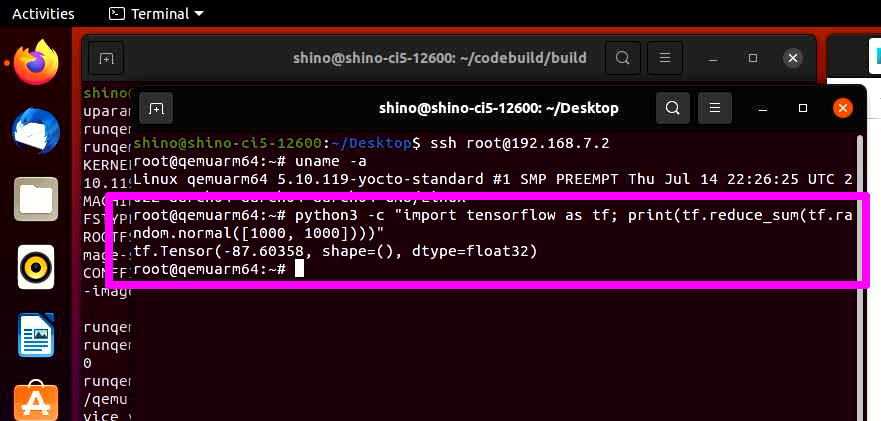
Gran Telescopio Canarias (GTC), the world’s largest single-aperture optical telescope, utilizes an extremely sophisticated computerized onboard system to capture secrets in the night sky. GTC is controlled by a high-capacity, high-performance IT architecture. A set of subsystems, physically distributed throughout the GTC, controls functions and compensates for the adverse effects of variables such as wind, temperature, hygrometry, distortion of parts, and vibration. A network of interconnected equipment, such as computers and sensors, supervises these subsystems and provides a homogenous user interface. The trick is to make all of this work together in real time.
“We chose Wind River’s VxWorks because we needed a sufficiently stable and high-performance real-time operating system so that we were free to concentrate on developing applications.”
—Martí Pi i Puig, Head of the Control Group, GTC Project
How Wind River Helped
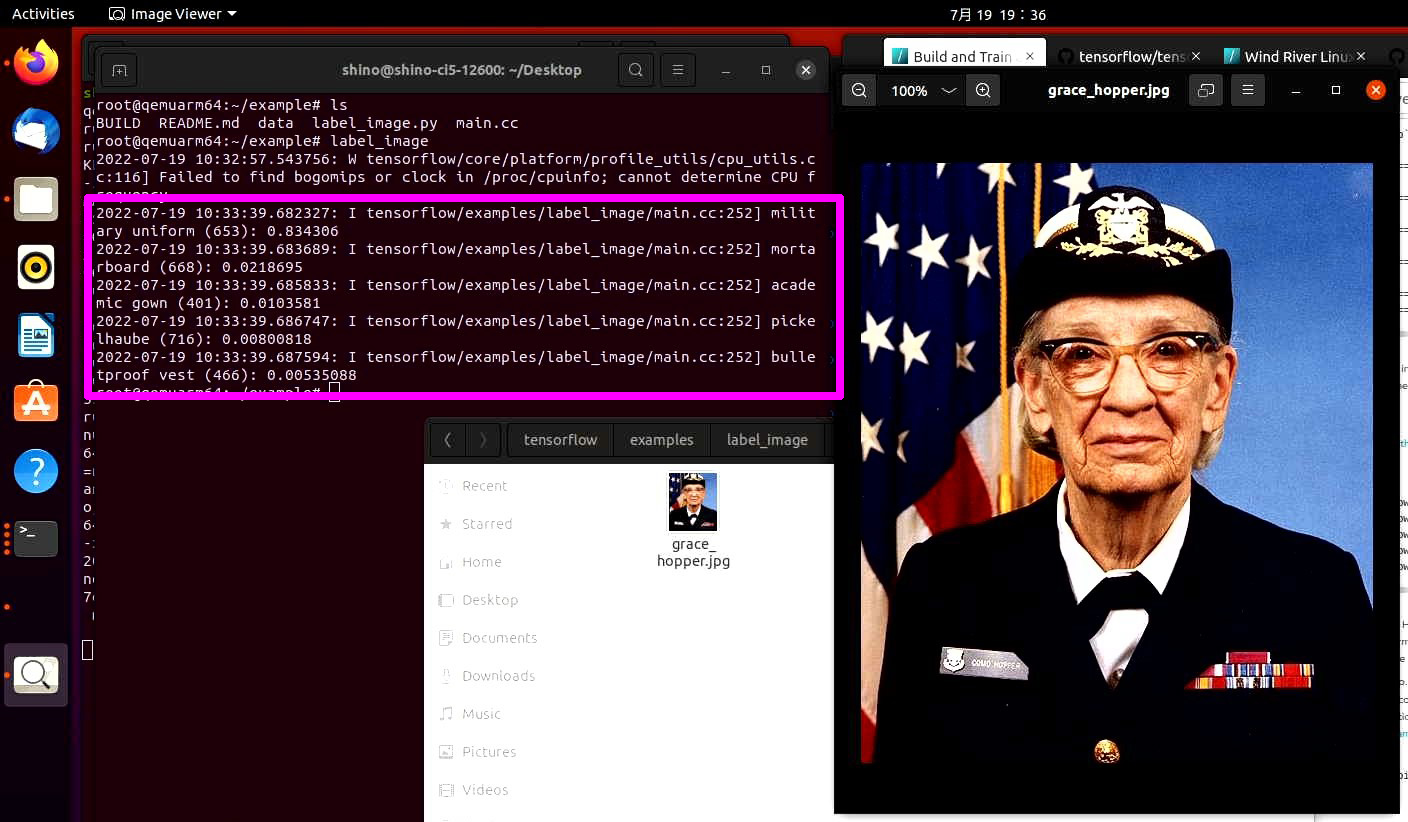
The GTC Control Group—a collaboration of Spain, Mexico, and the University of Florida—determined that traditional operating systems would not meet the requirements it had identified for the onboard computers. GTC Control Group selected VxWorks® because it would support the telescope’s stringent performance requirements. Many of the telescope's subsystems — such as motors, encoders, sensors, and cameras — require supervision on a material level and real-time results.
The Results
Astronomers from Spain, Mexico, and the U.S. have been coming to the Canary Islands since “first light” in 2009 to study the furthest and palest cosmic bodies in the universe with the largest telescope in existence. The VxWorks stable, high-performance real-time operating system has allowed these astronomers to concentrate on developing applications rather than spend time configuring components of the operating system or solving basic problems. Observation time is a precious commodity, and the scheduling of telescope time stretches out for years. VxWorks keeps the many disparate systems working in tight, real-time coordination. The rest is starlight.